The main outputs of the project

Efficient correction of SCD HSPCs with minimal impact on their properties and genome integrity

Catalogue of best practice tools and protocols for genome editing-based therapeutic approaches
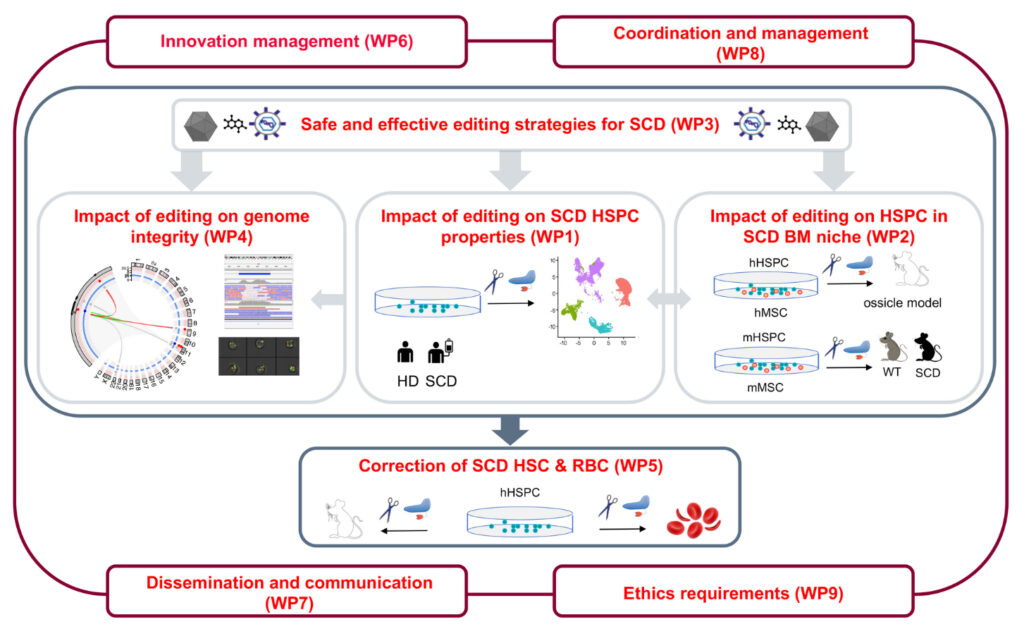
Workpackages
WP 1
Evaluation of the impact of different SCD genome editing approaches on SCD human HSPC cell-autonomous properties
To study and correct the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying SCD human HSPC (hHSPC) dysfunction, and analyze the impact of genome editing on SCD hHSPC cell-autonomous properties. Experiments will be carried out in SCD patient-derived and healthy donor (HD) hHSPC
WP 2
Evaluation of the impact of different SCD genome editing approaches on SCD HSPC non-cell-autonomous properties
To define the impact of different genome editing approaches on SCD HSPC functions, such as engraftment, expansion and interaction with niche components in the SCD bone marrow through:
- The identification of disease-specific features/dysfunctions of mice HSPC and stromal niche components in a SCD murine model and the impact of genome editing on hematopoietic stem cell(HSC) biology and function in the niche.
- The identification of disease-specific features/dysfunctions of SCD human mesenchymal stem cell (hMSC), their interactions with SCD hHSPC and the impact of genome editing on hHSPC-hMSC interactions
WP 3
Establishment of safe and effective genome editing approaches for SCD
To ameliorate precise genome editing in primary hHSPC through the optimization of several crucial aspects of the genome editing procedure by:
- Exploring different strategies to alter the normal resolution of a nuclease-induced double strand break (DSB) and reduce the mutational landscape resulted from unwanted indels during repair
- Establishing a DSB-free gene correction strategy for the SCD mutation using Cas9-nickases that introduce single strand breaks (SSB)
- Identifying the most effective repair template for genome editing in hHSPC in the context of DSB or SSB
WP 4
Evaluation of the outcomes and impact of different SCD genome editing approaches on genome integrity
To study the genotoxicity outcomes of genome editing approaches, based on non-homologous end-joining (NHEJ) by Cas9- nucleases, homology directed repair (HDR) editing by Cas9-nucleases and nickases, and base editors for SCD therapy through:
- The identification of putative off-target sites.
- The characterization and quantification of unwanted genetic variants.
- Identification, characterization and quantification of donor DNA integration events.
WP 5
Comparison of the most effective editing strategies in SCD human HSPC
To evaluate and compare editing strategies for SCD treatment in terms of correction of the sickle phenotype and extent of genetic modification in SCD patient-derived HSC.
WP 6
Innovation Management
To maximize the potential societal and scientific impact of EDITSCD by monitoring the generation of results and technology readiness during project execution by:
- developing a standardized invention disclosure process to identify key exploitable results and intellectual property throughout the project lifespan in a timely fashion
- developing an Innovation Management Plan that will guide the actions of the consortium with respect to sustainability and exploitation readiness of the project outputs
- Ensure stakeholder engagement for sustainability planning by interacting with the relevant partners and groups within the consortium and in the Genome Editing Community.
WP 7
Dissemination and communication
To disseminate the knowledge and scientific results generated from the project to all the different target groups (scientific community, health care providers, financial actors, patients, families, patient organizations and general public).
WP 8
Coordination and management
To ensure good scientific coordination among project partners, management of internal and external communication activities, and compliance with legal and contractual requirements.
WP 9
Ethics requirements
To ensure compliance with the ethics requirements within the project.